What about vitamins and minerals?
More than 6 out of 10 French people (62%) say they plan to buy food supplements soon, particularly vitamins and minerals (39%) (OpinionWay for Synadiet, 2020).
What are vitamins and minerals used for? How are they framed? What do the health authorities think?
Vitamins and minerals, their major functions and their dosage in food supplements
Minerals
Calcium, magnesium, phosphorus, sodium, iron, zinc and selenium are among the most famous minerals.
The quantities of mineral matter in the body are very variable: almost 1 kg for calcium and phosphorus, a few grams for iron, zinc and fluorine and less than 1 mg for chromium and cobalt. In total, mineral elements represent about 4% of body weight but are involved in a wide range of functions: mineralisation, control of water balance, enzymatic and hormonal systems, nervous, muscular and immune systems (ANSES).
A balanced and diversified diet guarantees the supply of minerals and compensates for daily losses. Food supplements are used as a winter cure or in case of a need for supplementation on medical prescription.
Vitamins
Vitamins are substances without energy value but essential for the body. These substances are necessary for many physiological processes. Except for two of them (vitamins K and D), the human body is unable to produce them. Therefore, their intake through food is essential for the healthy functioning of our organism (ANSES).
Vitamin C is certainly the most widely known to the public for its anti-oxidant and immune system role. It is present in all plants.
This vitamin is found in many food supplements. It is also used in nutricosmetics. The following claim is authorised by EFSA: ” Vitamin C contributes to normal collagen formation for the normal function of skin”.
Certain vitamins play an essential role in the absorption of minerals. This is the case, for example, with vitamin D, which increases the concentrations of calcium and phosphorus in the blood (bone mineralisation, coagulation, etc.). Vitamin D is supplied both by the diet and by the body through the skin under the action of the sun’s rays. Certain populations may be at risk of vitamin D deficiency: newborns, infants, pregnant women and the elderly (non-autonomous), who have little exposure to the sun and/or have increased needs. Supplementation is often recommended for certain northern populations with low exposure.
Traditionally, vitamins are classified in 2 categories:
– Fat-soluble vitamins: A, D, E, K. They are stored in adipose tissue (D, E) and in large quantities in the liver (A). Their intake must be controlled to avoid overdosage.
– Water-soluble vitamins: vitamins of the B group (B1, B2, B3 or PP, B5, B6, B8, B9 and B12) and vitamin C. There is less risk of overdose (elimination in the urine).
Dosage of vitamins and minerals in food supplements
While food supplements can be used to correct nutritional deficiencies or maintain an adequate intake, an excess of vitamins and minerals can have an undesirable or even toxic effect. France has established maximum daily doses. In addition, the European Union (EU) has introduced harmonised rules to help ensure that food supplements are safe and properly labelled.
Vitamins, minerals and immunity
Vitamins A, C, B6, B9, B12, D, copper, iron, zinc, selenium are essential vitamins and trace elements for the immune system.
Europe recognises that these vitamins and minerals contribute to the normal function of the immune system (EFSA, Regulation (EU) No 432/2012). Their dosage is also defined.
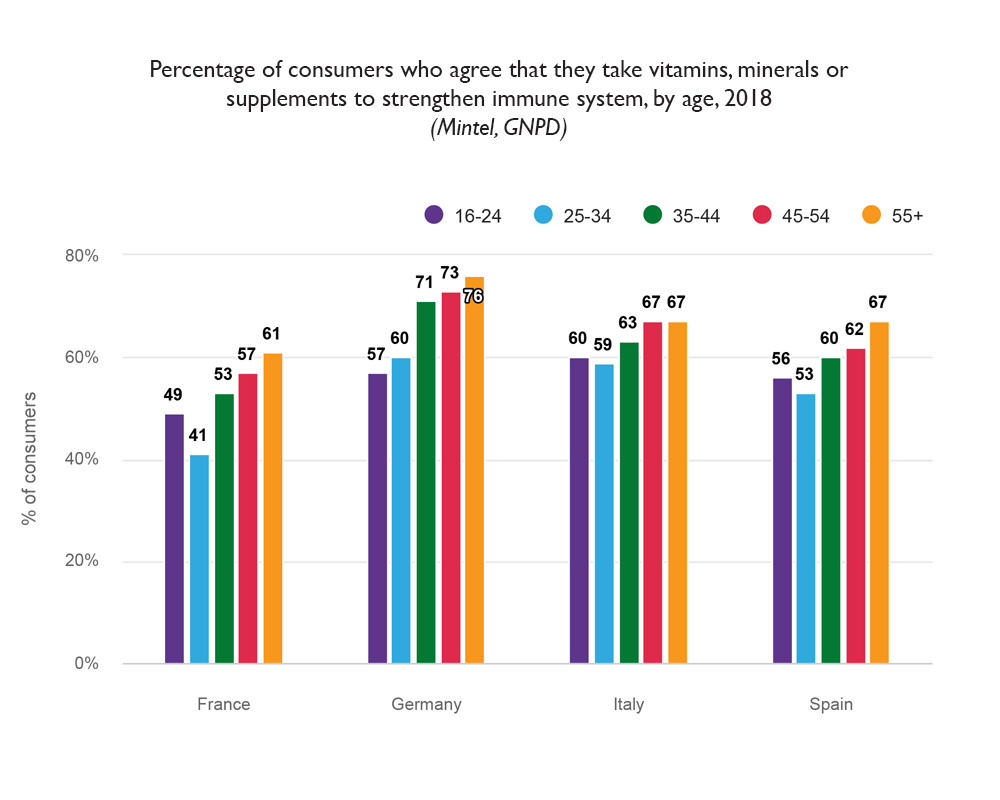
In Europe, most people take vitamins, minerals or supplements to improve immune function.
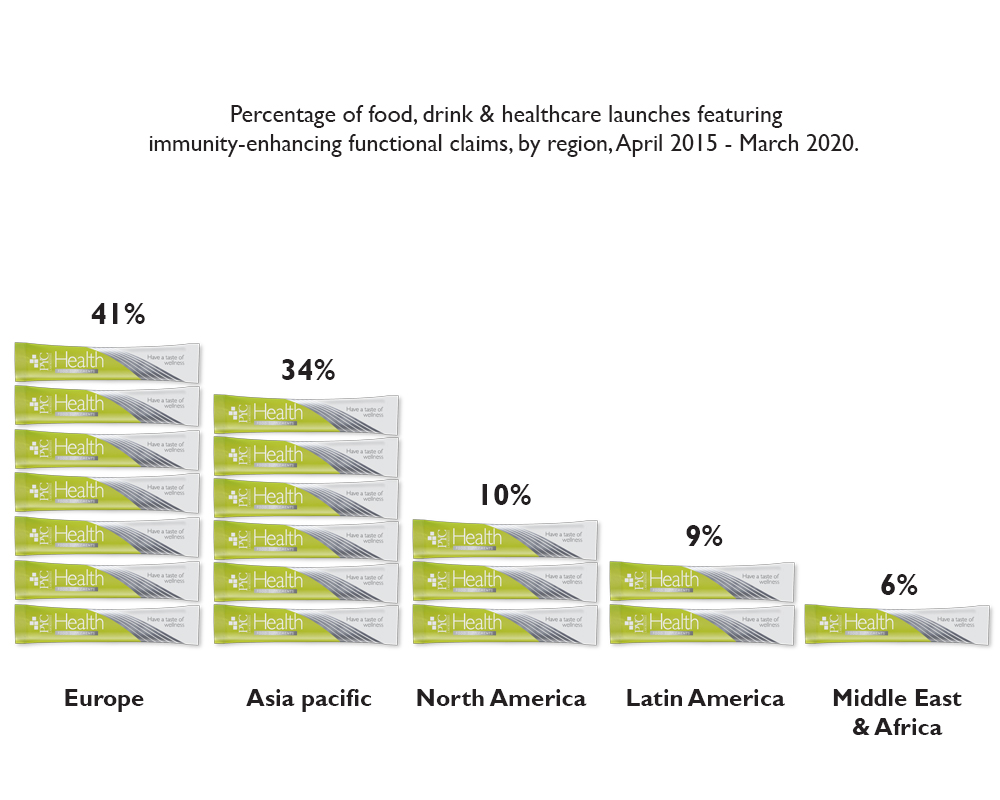
In fact, the European market has launched the most immunity boosting products in the last five years.
At Laboratoire PYC, we work on innovative immunity food supplement formulas. We offer several galenics (sticks, jars, stand-up pouches). We have recently added new immunity active ingredients to our range. To be discovered !
To request your immunity food supplement formula:
- Posted In:
- News







